Industrial Servo Motor
A servo motor is an electric motor that provides precise control of angular or linear position, speed, and torque using a feedback loop system. It consists of three main components:
Motor: The motor can be either a DC motor or an AC motor, depending on the power source and application requirements. It provides the mechanical power to rotate or move the output shaft.
Encoder: The sensor measures the position, speed, or torque of the output shaft and sends feedback signals to the controller. Common sensor types include potentiometers, encoders, and resolvers.
Drive: The controller compares the feedback signals from the encoder with desired setpoint signals (from an external source like a computer or joystick). It generates control signals to adjust the motor’s voltage or current, maintaining accuracy and alignment with the desired setpoint.
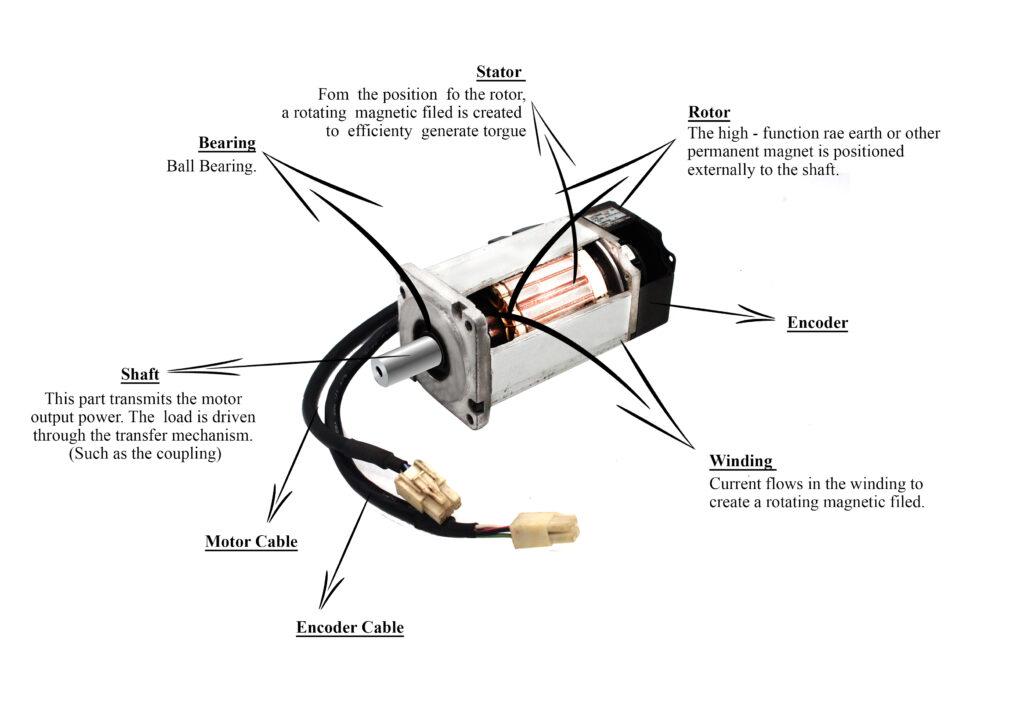
- Stator From the position of the rotor, a rotating magnetic field is created to efficiently generate torque
- Winding Current flows in the winding to create a rotating magnetic field.
- Bearing Ball Bearing
- Shaft This part transmits the motor output power. The load is driven through the transfer mechanism (such as the coupling).
- Rotor A high-function rare earth magnet or another permanent magnet is positioned externally to the shaft.
- Encoder The optical encoder always watches the number of rotations and the position of the shaft.
- Encoder Cable
- Motor Cable

A servo motor encoder is a crucial component in a servomechanism, which is a system used to automate mechanical motion with high precision.
The encoder is a sensor that notifies the driver, that the speed and position of the motor. The encoders (position detectors) used in the servo motor can be structurally classified as “incremental encoders” and “absolute encoders”.
How Servo Motor Encoders Work?
Motor encoders consist of two main parts:
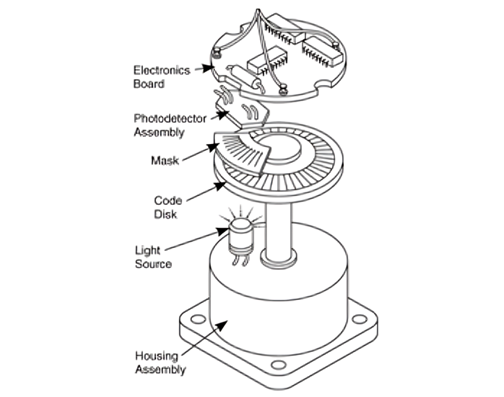
- Shaft: The encoder attaches to the motor shaft. As the shaft rotates, it transmits motion to the encoder’s internal components.
- Disc (Code Wheel): The disc also mounts to the motor shaft. It contains patterns or markings that interact with sensors to generate electrical signals.
The encoder serves as a sensor for detecting both the speed and position of the motor. Light emitted from the light-emitting diode (LED) passes through a position detection pattern on the slit disk and is then captured by the photo diode. Within the photo diode, numerous photo transistors are integrated. The various patterns used for absolute position detection rely on the encoder’s rotation angle. Additionally, a microprocessor is mounted on the encoder to analyse the absolute position detection patterns. Finally, the current position data is transmitted to the servo driver via serial communication.
A servo motor encoder detects:
- Rotation Angle: The position of the moving machine part.
- Speed: How fast the part is moving.
- Travel Distance: The distance covered by the part.
Related Products
View All

Add to Wishlist Add to Wishlist
Compare
MFA100MBYNF
Enquiry In Stock 
Add to Wishlist Add to Wishlist
Compare
MFA100MBYNF
Enquiry In Stock 
Add to Wishlist Add to Wishlist
Compare
AK M 22E -ANB2R-00
Enquiry In Stock 
Add to Wishlist Add to Wishlist
Compare
AK M 22E -ANB2R-00
Enquiry In Stock 
Add to Wishlist Add to Wishlist
Compare
AK M 22E -ANB2R-00
Enquiry In Stock 
Add to Wishlist Add to Wishlist
Compare
CFM90L4/BR/TF/AKIH/S850
Enquiry In Stock 
Add to Wishlist Add to Wishlist
Compare
AKM41H-ACSN2-02
Enquiry In Stock 
Add to Wishlist Add to Wishlist
Compare
AKM43G-ACSN2-02
Enquiry In Stock
- Image
- SKU
- Rating
- Price
- Stock
- Availability
- Add to cart
- Description
- Content
- Weight
- Dimensions
- Additional information