Introduction To Industrial Ac Servo Drive
A industrial servo drive is an electronic device designed to control the motion of a servo motor. Servo motors are specialized motors capable of precise control over position, speed, and torque, making them ideal for applications where accuracy is paramount. Servo drive is the most important part of the servo system. It plays an important role in controlling the servo motor. A servo drive is used to drive an servo motor that receives signals from the control system, amplifies them and sends power to the servo motor. It enables the generation of signals related to the predicted signals. The servo drive follows the feedback signal from the feedback device (servo motor encoder).

Functions of servo drive
The servo drive automatically adjusts the voltage, frequency or pulse width at the motor to correct any output of the specified voltage. In a precision control system, the servo motor rotates at a speed close to the speed signal that the servo system receives from the control system. Many parameters, such as stiffness (also known as gain ratio), shrinkage (also known as yield gain), and feedback gain, can be adjusted to achieve the desired performance. The process of changing the parameters is called correlation function. While many servo motors require a specific driver for that brand or motor, there are many drivers available today that fit a variety of motors.
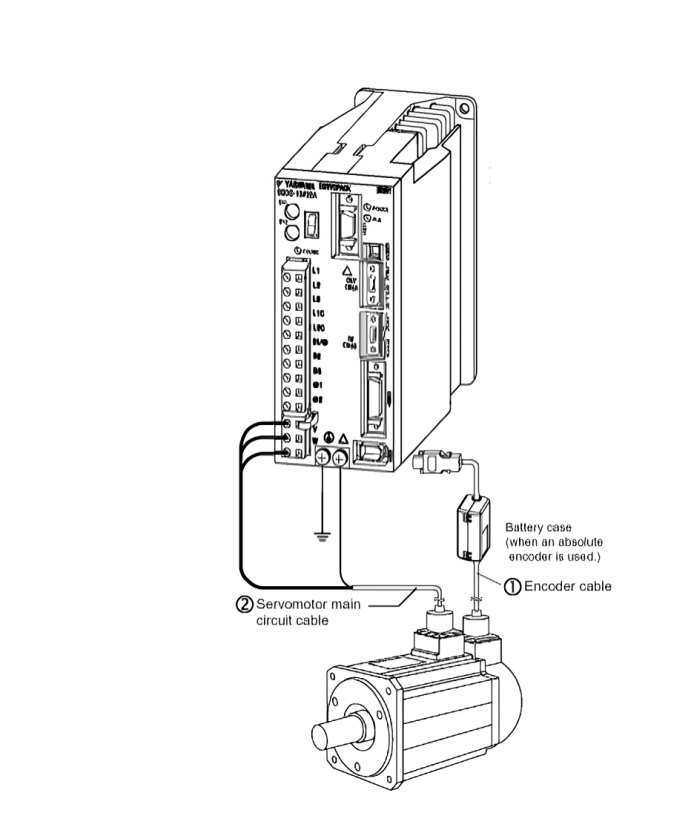
Working stages of servo drive
Servo drives operate based on a closed-loop control system, which means they continuously receive feedback about the motor’s actual position and adjust the motor’s operation to match the desired position.
- Command Input: The servo drive receives commands from a controller, such as a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) or a computer, specifying the desired motion parameters, such as position, speed, and acceleration.
- Feedback Loop: The servo drive continuously receives feedback from sensors, such as encoders or resolvers, attached to the servo motor. These sensors provide information about the motor’s actual position, speed, and other parameters.
- Error Calculation: The servo drive compares the commanded motion parameters with the feedback from the sensors to calculate any errors in position, speed, or torque.
- Control Signal Generation: Based on the calculated errors, the servo drive generates control signals to adjust the power supplied to the servo motor. These control signals ensure that the motor moves in the desired manner to minimize the errors.
- Motor Control: The servo drive sends the adjusted power signals to the servo motor, causing it to move according to the specified parameters. The motor’s movement is continuously monitored and adjusted to maintain precise control over motion.
Applications of Servo Drive
Servo drives are generally used to control the speed, position and torque of electric servo motor. They are available in different sizes and are suitable for static and mobile applications in many industries, like:
- CNC Machines: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines use servo drives to precisely control the movement of cutting tools, ensuring accurate machining of parts.
- Robotic Arms: Servo drives power the movements of robotic arms in manufacturing processes, such as pick-and-place operations, welding, and assembly.
- Conveyor Systems: Servo drives control the speed and position of conveyor belts in material handling systems, optimizing throughput and reducing errors.
2. Packaging:
- Filling Machines: Servo drives precisely control the filling of containers in packaging machinery, ensuring accurate dosing of liquids or granular products.
- Labeling Machines: Servo drives control the positioning of labels on packaging, allowing for precise application even at high speeds.
- Cartoners and Case Packers: Servo drives control the movement of cartons and cases in packaging lines, facilitating smooth and precise packaging operations.
3. Printing and Labeling:
- Digital Printers: Servo drives control the movement of printheads in digital printers, enabling high-resolution printing with precise registration.
- Label Printers/Applicators: Servo drives control the positioning of labels for printing or application onto products or packaging.
4. Textile Industry:
- Weaving Machines: Servo drives control the movement of the shuttle and the positioning of the yarn in weaving machines, ensuring precise fabric production.
- Knitting Machines: Servo drives control the movement of knitting needles, allowing for the creation of intricate patterns and designs in knitted fabrics.
5. Automotive Manufacturing:
- Assembly Lines: Servo drives are used in various stages of automotive assembly, including welding, painting, and assembly of components, ensuring precise positioning and movement of parts.
- Testing Equipment: Servo drives control the movement of test rigs and equipment used for quality control and testing of automotive components.
6. Aerospace Industry:
- Flight Control Systems: Servo drives are crucial components of flight control systems, controlling the movement of control surfaces such as ailerons, elevators, and rudders in aircraft.
- Satellite Positioning: Servo drives are used in satellite positioning systems to accurately orient antennas and solar panels.
7. Medical Equipment:
- Surgical Robots: Servo drives enable precise control of robotic arms in surgical robots, allowing surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with high accuracy.
- Diagnostic Equipment: Servo drives control the movement of components in medical imaging equipment, such as CT scanners and MRI machines, ensuring accurate image acquisition.
Advantages of Servo Drives
- Precision: Servo drives offer precise control over position, speed, and torque, allowing for accurate and repeatable motion.
- Flexibility: They can handle a wide range of motion profiles and loads, making them suitable for diverse applications.
- Energy Efficiency: Servo drives consume power only as needed, leading to energy savings compared to other motor control methods.
- Response Time: Servo systems can respond rapidly to changes in commands, enabling quick adjustments in motion.
- Image
- SKU
- Rating
- Price
- Stock
- Availability
- Add to cart
- Description
- Content
- Weight
- Dimensions
- Additional information